Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Riyana, E. S.; Okumura, Keisuke; Sakamoto, Masahiro; Matsumura, Taichi; Terashima, Kenichi; Kanno, Ikuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 8 Pages, 2024/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.18(Nuclear Science & Technology)Fukahori, Tokio
INDC(JPN)-210 (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/10
The  U(n,f) cross section values were not correctly compiled in the ENDF format, and wrong values are disseminated in the JENDL/HE-2007 file. The high energy part of the
U(n,f) cross section values were not correctly compiled in the ENDF format, and wrong values are disseminated in the JENDL/HE-2007 file. The high energy part of the  U(n,f) cross section for the JENDL/HE-2007 library was evaluated by using the results of the FISCAL code. The correct
U(n,f) cross section for the JENDL/HE-2007 library was evaluated by using the results of the FISCAL code. The correct  U(n,f) cross section values of the JENDL/HE-2007 library above 200 MeV is given in this report.
U(n,f) cross section values of the JENDL/HE-2007 library above 200 MeV is given in this report.
Rodriguez, D.; Abbas, K.*; Bertolotti, D.*; Bonaldi, C.*; Fontana, C.*; Fujimoto, Masami*; Geerts, W.*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Macias, M.*; Nonneman, S.*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Annual Meeting 2023 (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/05
 , Zr, and stainless steel and leaching behavior of the fission products and matrix elements
, Zr, and stainless steel and leaching behavior of the fission products and matrix elementsTonna, Ryutaro*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kodama, Yuji*; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kumagai, Yuta; Kusaka, Ryoji; Watanabe, Masayuki
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 55(4), p.1300 - 1309, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)Simulated debris was synthesized using UO , Zr, and stainless steel and a heat treatment method under inert or oxidizing conditions. The primary U solid phase of the debris synthesized at 1473 K under inert conditions was UO
, Zr, and stainless steel and a heat treatment method under inert or oxidizing conditions. The primary U solid phase of the debris synthesized at 1473 K under inert conditions was UO , whereas a (U,Zr)O
, whereas a (U,Zr)O solid solution formed at 1873 K. Under oxidizing conditions, a mixture of U
solid solution formed at 1873 K. Under oxidizing conditions, a mixture of U O
O and (Fe,Cr)UO
and (Fe,Cr)UO phases formed at 1473 K whereas a (U,Zr)O
phases formed at 1473 K whereas a (U,Zr)O solid solution formed at 1873 K. The leaching behavior of the fission products from the simulated debris was evaluated using two methods: the irradiation method, for which fission products were produced via neutron irradiation, and the doping method, for which trace amounts of non-radioactive elements were doped into the debris. The dissolution behavior of U depended on the properties of the debris and aqueous medium the debris was immersed in. Cs, Sr, and Ba leached out regardless of the primary solid phases. The leaching of high-valence Eu and Ru ions was suppressed, possibly owing to their solid-solution reaction with or incorporation into the uranium compounds of the simulated debris.
solid solution formed at 1873 K. The leaching behavior of the fission products from the simulated debris was evaluated using two methods: the irradiation method, for which fission products were produced via neutron irradiation, and the doping method, for which trace amounts of non-radioactive elements were doped into the debris. The dissolution behavior of U depended on the properties of the debris and aqueous medium the debris was immersed in. Cs, Sr, and Ba leached out regardless of the primary solid phases. The leaching of high-valence Eu and Ru ions was suppressed, possibly owing to their solid-solution reaction with or incorporation into the uranium compounds of the simulated debris.
 /
/ /
/ -rays radiolysis (Contract research); FY2021 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project
-rays radiolysis (Contract research); FY2021 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development ProjectCollaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2022-069, 114 Pages, 2023/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of a new corrosion mitigation technology using nanobubbles toward corrosion mitigation in PCV system under the influence of  /
/ /
/ -rays radiolysis" conducted in FY2021. In this work, in order to ensure the long-term reliability of steel structures that ensure important confinement functions in the debris removal process, such as existing PCVs and newly constructed negative pressure maintenance systems and piping, corrosion phenomena in wet environments where
-rays radiolysis" conducted in FY2021. In this work, in order to ensure the long-term reliability of steel structures that ensure important confinement functions in the debris removal process, such as existing PCVs and newly constructed negative pressure maintenance systems and piping, corrosion phenomena in wet environments where  - and
- and  -ray emitting nuclides come into contact with steel are clarified for the first time.
-ray emitting nuclides come into contact with steel are clarified for the first time.
Mohamad, A. B.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Miwa, Shuhei; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(3), p.215 - 222, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2022-053, 89 Pages, 2023/02
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Uncertainty reduction of the FPs transport mechanism and debris degradation behavior and evaluation of the reactor contamination of debris state on the basis of the accident progression scenario of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Unit 2 and 3" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to elucidate the cause of the high dosage under shield plug by clarification of to the cesium behavior of migration, adhesion to structure and deposition as well as evaluate the properties of metal-rich debris predeceasing melted through the materials science approach based on the most probable scenario of accident progression of Unit 2 and 3. In this fiscal year, the followings were achieved.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2022-009, 73 Pages, 2022/06
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Basic research on the stability of fuel debris including alloy phase" conducted from FY2018 to FY2021 (this contract was extended to FY2021). Since the final year of this proposal was FY2021, the results for four fiscal years were summarized. The present study focus on fuel debris consisting of oxide phase and alloy phase generated by the high temperature chemical reaction between structure materials (SUS pipes, pressure vessels, etc.) and fuels (melted fuels, claddings components, etc.). We synthesize the simulated debris of UO -SUS system and UO
-SUS system and UO -Zr(ZrO
-Zr(ZrO )-SUS system by high-temperature heat treatment, and measure their chemical property and dissolution behavior in water.
)-SUS system by high-temperature heat treatment, and measure their chemical property and dissolution behavior in water.
 /
/ /
/ -rays radiolysis (Contract research); FY2020 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project
-rays radiolysis (Contract research); FY2020 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development ProjectCollaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2022-002, 85 Pages, 2022/06
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of a new corrosion mitigation technology using nanobubbles toward corrosion mitigation in PCV system under the influence of  /
/ /
/ -rays radiolysis" conducted in FY2020. In this work, in order to ensure the long-term reliability of steel structures that ensure important confinement functions in the debris removal process, such as existing PCVs and newly constructed negative pressure maintenance systems and piping, corrosion phenomena in wet environments where
-rays radiolysis" conducted in FY2020. In this work, in order to ensure the long-term reliability of steel structures that ensure important confinement functions in the debris removal process, such as existing PCVs and newly constructed negative pressure maintenance systems and piping, corrosion phenomena in wet environments where  - and
- and  -ray emitting nuclides come into contact with steel are clarified for the first time.
-ray emitting nuclides come into contact with steel are clarified for the first time.
Maekawa, Fujio
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 98(5), p.201 - 205, 2022/05
The nuclear transmutation technology is a powerful solution to the "nuclear waste" problem that accompanies nuclear power generation. The Accelerator Driven System (ADS), which combines a high-intensity accelerator and a subcritical core, is a promising tool for nuclear transmutation. In this paper, we will explain the significance and principle of nuclear transmutation by ADS, design examples of ADS, partitioning and transmutation technology and its effects, required performance of high-intensity accelerators, overseas trends, etc.
Riyana, E. S.; Okumura, Keisuke; Sakamoto, Masahiro; Matsumura, Taichi; Terashima, Kenichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(4), p.424 - 430, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:16.35(Nuclear Science & Technology)Lind, T.*; Herranz, L. E.*; Sonnenkalb, M.*; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of 19th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-19) (Internet), 15 Pages, 2022/03
Rizaal, M.; Miwa, Shuhei; Suzuki, Eriko; Imoto, Jumpei; Osaka, Masahiko; Gou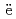 llo, M.*
llo, M.*
ACS Omega (Internet), 6(48), p.32695 - 32708, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.77(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Lind, T.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Herranz, L. E.*; Sonnenkalb, M.*; Nishi, Yoshihisa*; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Cousin, F.*; Fernandez Moguel, L.*; Andrews, N.*; Sevon, T.*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 376, p.111138_1 - 111138_12, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:93.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)This is the third part of the three part paper describing the accidents at the FDNPS as analyzed in the Phase 2 of the OECD/NEA project "Benchmark Study of the Accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant" (BSAF). In this paper, we describe the accident progression in unit 3. In the BSAF project, eight organizations from five countries analyzed severe accident scenarios for Unit 3 at the Fukushima Daiichi site using different severe accident codes. The present paper for Unit 3 describes the findings of the comparison of the participants' results against each other and against plant data, the evaluation of the accident progression and the final status inside the reactors. Special focus is on the status of the reactor pressure vessel, melt release and fission product release and transport. Unit 3 specific aspects, e.g., the complicated accident progression following repeated containment venting actuations and attempts at coolant injection at the time of the major core degradation, are highlighted and points of consensus as well as remaining uncertainties and data needs will be summarized. FP transport is analyzed, and the calculation results are compared with dose rate measurements in the containment. The release of I-131 and Cs-137 to the environment is compared with analysis conducted by using WSPEEDI code.
Rodriguez, D.; Bogucarska, T.*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Lee, H.-J.; Pedersen, B.*; Rossi, F.; Takahashi, Tone; Varasano, G.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 997, p.165146_1 - 165146_13, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.91(Instruments & Instrumentation)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2020-032, 97 Pages, 2021/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2019. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Basic Research on the Stability of Fuel Debris Including Alloy Phase" conducted in FY2019. In the present study, we focus on fuel debris consisting of oxide phase and alloy phase generated by the high-temperature chemical reaction between structure materials (SUS pipes, pressure vessels, etc.) and fuels (melted fuels, claddings components, etc.). We synthesize the simulated debris of UO -SUS system and UO
-SUS system and UO -Zr(ZrO
-Zr(ZrO )-SUS system by high-temperature heat treatment, and measure their chemical property and dissolution behavior in water. Also, we will conduct research and development to spectroscopically analyze secular changes of oxide phase and alloy phase in the simulated debris.
)-SUS system by high-temperature heat treatment, and measure their chemical property and dissolution behavior in water. Also, we will conduct research and development to spectroscopically analyze secular changes of oxide phase and alloy phase in the simulated debris.
Kitamura, Akira; Akahori, Kuniaki; Nagata, Masanobu*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 27(2), p.83 - 93, 2020/12
Direct disposal of spent nuclear fuel (SNF) in deep underground repositories (hereafter "direct disposal") is a concept that disposal canisters stored fuel assemblies dispose without reprocessing. Behavior of radionuclide release from SNF must be different from that from vitrified glass. The present study established a methodology on determination of instant release fraction (IRF) of radionuclides from SNF, which is the one of the parameters on radionuclide release based on the latest safety assessment reports in other countries, especially for IRF values proportional to a fission gas release ratio (FGR). Recommended and maximum values of FGR have been estimated using the fuel performance code FEMAXI-7 after collecting FGR values on Japanese SNFs. Furthermore, recommended and maximum values of IRF for Japanese SNFs used in a pressurized water reactor (PWR) have been estimated using the presently obtained FGR values and experimentally obtained IRF values on foreign SNFs. The recommended and maximum IRF values obtained in the present study have been compared with those of the latest safety assessment reports in other countries.
Miyahara, Naoya; Miwa, Shuhei; Gou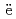 llo, M.*; Imoto, Jumpei; Horiguchi, Naoki; Sato, Isamu*; Osaka, Masahiko
llo, M.*; Imoto, Jumpei; Horiguchi, Naoki; Sato, Isamu*; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(12), p.1287 - 1296, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:53.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to clarify the cesium iodide (CsI) transport behavior with a focus on the mechanisms of gaseous iodine formation in the reactor coolant system of LWR under a severe accident condition, a reproductive experiment of CsI transport behavior was conducted using a facility equipped with a thermal gradient tube. Various analyses on deposits and airborne materials during transportation could elucidate two mechanisms for the gaseous iodine formation. One was the gaseous phase chemical reaction in Cs-I-O-H system at relatively high-temperature region, which led to gaseous iodine transport to the lower temperature region without any further changes in gas species due to the kinetics limitation effects. The other one was the chemical reactions related to condensed phase of CsI, namely those of CsI deposits on walls with surface of stainless steel to form Cs CrO
CrO compound and CsI aerosol particles with steam, which were newly found in this study.
compound and CsI aerosol particles with steam, which were newly found in this study.
Miwa, Shuhei; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Miyahara, Naoya; Nishioka, Shunichiro; Suzuki, Eriko; Horiguchi, Naoki; Liu, J.; Miradji, F.; Imoto, Jumpei; Afiqa, B. M.; et al.
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 7(3), p.19-00537_1 - 19-00537_11, 2020/06
We constructed the fission product (FP) chemistry database named ECUME for LWR severe accident. This version of ECUME is equipped with dataset of the chemical reactions and their kinetics constants for the reactions of cesium(Cs)-iodine(I)-boron(B)-molybdenum(Mo)-oxygen(O)-hydrogen(H) system in gas phase, the elemental model for the high temperature chemical reaction of Cs with stainless steel applied as the structural material in a reactor, and thermodynamic data for CsBO vapor species and solids of Cs
vapor species and solids of Cs Si
Si O
O and CsFeSiO
and CsFeSiO for these chemical reactions. The ECUME will provide estimation of Cs distribution due to the evaluation of effects of interaction with BWR control material B and stainless steel on Cs behavior in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station.
for these chemical reactions. The ECUME will provide estimation of Cs distribution due to the evaluation of effects of interaction with BWR control material B and stainless steel on Cs behavior in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2019-035, 61 Pages, 2020/03
JAEA/CLADS, had been conducting the Center of World Intelligence Project for Nuclear Science/Technology and Human Resource Development (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2018. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Basic Research on the Stability of Fuel Debris Including Alloy Phase". In the present study, we focus on fuel debris consisting of oxide phase and alloy phase generated by the high-temperature chemical reaction between structure materials (SUS pipes, pressure vessels, etc.) and fuels (melted fuels, claddings components, etc.). We synthesize the simulated debris of UO -SUS system and UO
-SUS system and UO -Zr(ZrO
-Zr(ZrO )-SUS system by high-temperature heat treatment, and measure their chemical property and dissolution behavior in water. Also, we will conduct research and development to spectroscopically analyze secular changes of oxide phase and alloy phase in the simulated debris.
)-SUS system by high-temperature heat treatment, and measure their chemical property and dissolution behavior in water. Also, we will conduct research and development to spectroscopically analyze secular changes of oxide phase and alloy phase in the simulated debris.